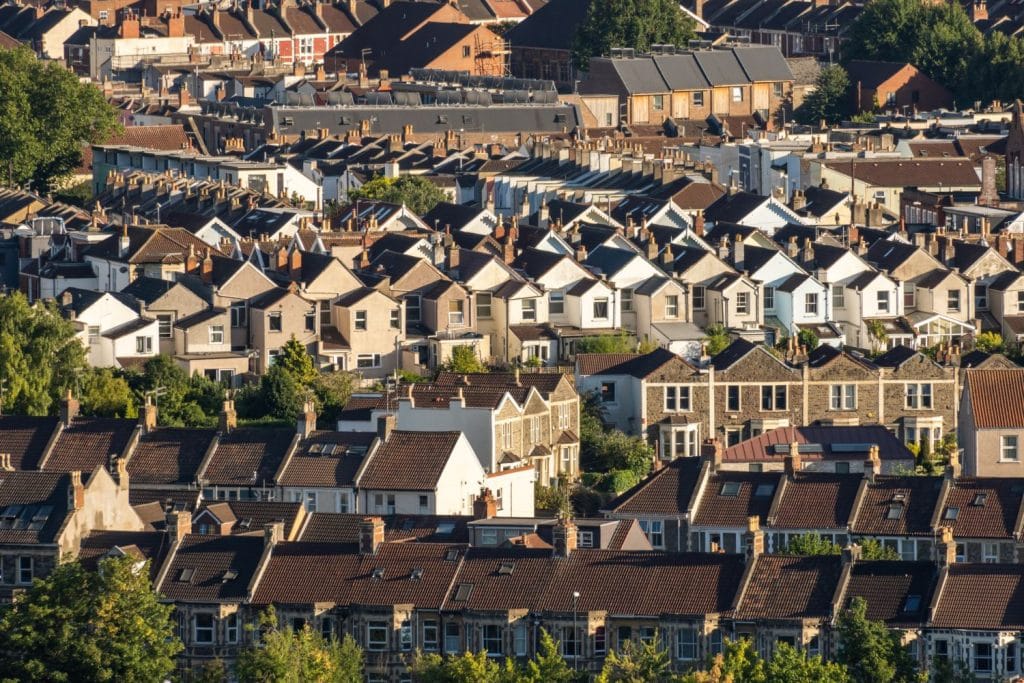
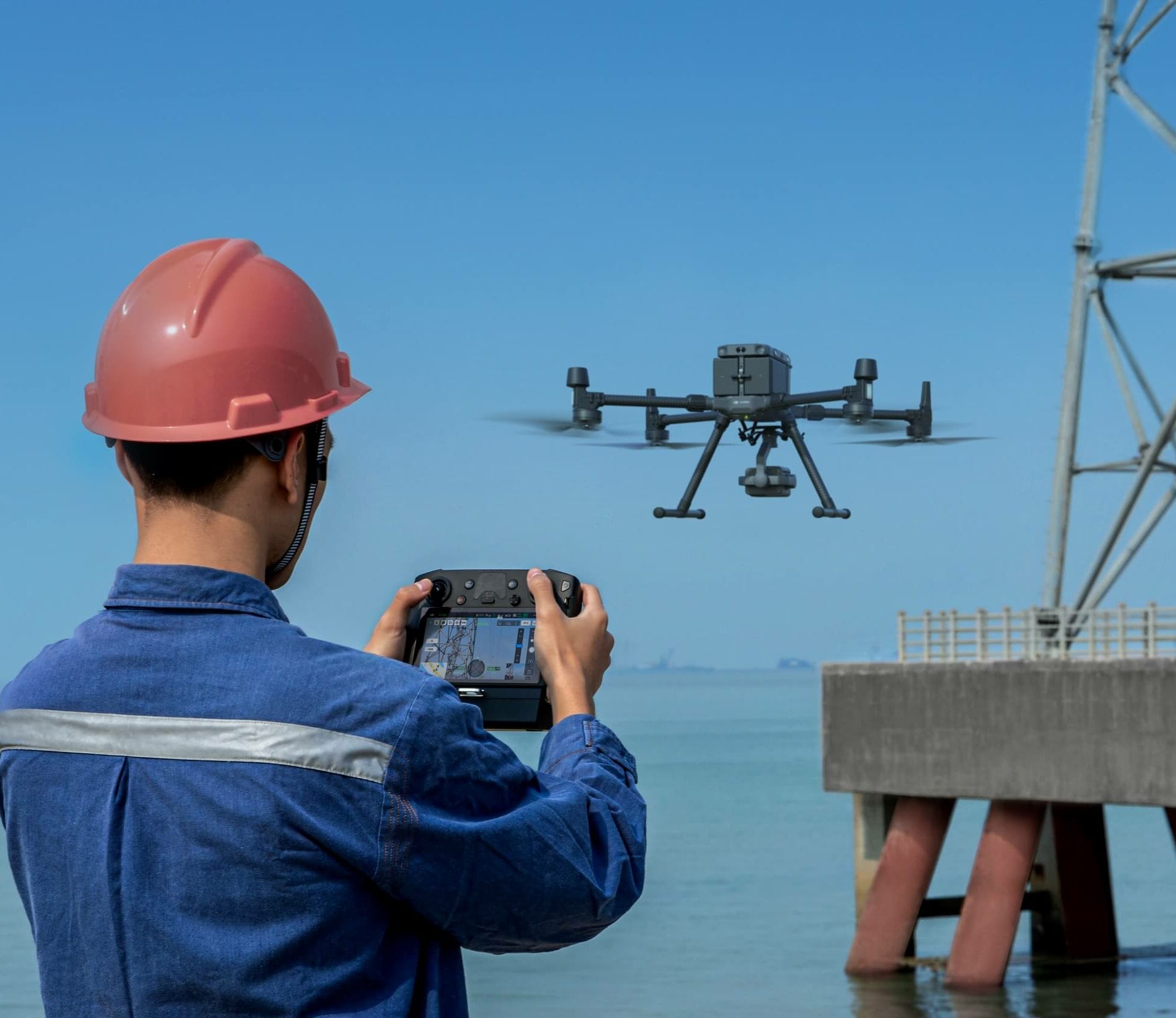
Yes, you can fly a drone over private property or land in the UK, but it is subject to specific regulations that ensure safety, privacy, and compliance with the law. To help you navigate these rules and operate drones responsibly, this guide covers everything you need to know about flying a drone over private property or land, including legal requirements, permission for takeoff and landing, privacy concerns, and more.
What Are the Rules for Flying a Drone Over Private Property in the UK?
Flying a drone over private property in the UK is legal, but it comes with a set of essential regulations. Operators must adhere to rules set by the Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) to ensure safety and protect privacy.
Key Regulations for Drone Flight Over Private Property:
- Altitude Limit: Drones must be flown below 400 feet (120 metres) to avoid interference with manned aircraft.
- Distance: Maintain a 50-metre distance from people, vehicles, and buildings that are not under your control.
- Line of Sight: Always keep the drone within your visual line of sight while flying.
- Restricted Areas: Avoid flying over congested areas, airports, or other restricted zones.
By adhering to these regulations, drone operators can ensure their flights are safe and legal when flying over private land.
Do I Need Permission to Fly a Drone Over Private Property or Land in the UK?
Yes, while it is legal to fly a drone over private property or land in the UK, you must obtain permission from the landowner to take off or land on their property. Without explicit consent, this could be considered trespassing.
Permission for Takeoff and Landing:
- Takeoff: Always seek permission from the landowner if you plan to take off from their property.
- Landing: Ensure you have landowner consent before landing your drone on their property.
Whether conducting a Drone land survey or typographic survey, explain your purpose clearly to the property owner.
At Sky Scan Surveys, we prioritize getting the necessary permissions from property owners to ensure we comply with the law and respect their rights.
What Privacy Laws Apply When Flying a Drone Over Private Property?
When operating drones with cameras over private property, privacy laws are a crucial consideration. In the UK, this includes compliance with GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation).
Key Privacy Considerations:
- Personal Data: If your drone captures footage that can identify individuals or private property, it is considered personal data under GDPR.
- Consent: You must inform individuals if their personal data is being captured by your drone and obtain explicit consent if necessary.
- Data Protection: Ensure that footage is stored securely and that sensitive data is handled responsibly.
Blur Faces and Personal Information:
To avoid privacy issues, always blur identifiable information such as faces and vehicle registration plates in your drone footage.
What Are the Legal Height and Distance Limits for Drones in the UK?
The UK has strict altitude and distance limits for drones to ensure safe operation and reduce the risk of accidents.
Altitude Limits:
- Drones must be flown below 400 feet (120 metres) to avoid interference with manned aircraft and ensure public safety.
Distance Requirements:
- Maintain a 50-metre distance from people, vehicles, and buildings not under your control.
- For congested areas, the distance may need to be increased to 150 meters horizontally to ensure safety and compliance with regulations.
How to Stay Compliant with CAA Regulations When Flying Drones
To operate a drone legally in the UK, you must follow CAA regulations and ensure that all necessary certifications are in place.
CAA Drone Registration:
- Drones with cameras or those over a specific weight must be registered with the Civil Aviation Authority.
Competency Test:
- Drone operators must pass a competency test like the DMARES (Drone and Model Aircraft Registration and Education Service) test to ensure they understand the legal and safety requirements.
Drone Insurance:
- Ensure that you have drone insurance to cover third-party damages and accidents. It’s mandatory for all operators to have insurance that covers potential liabilities.
What Happens If You Don’t Get Permission to Fly a Drone Over Private Property or Land?
If you operate a drone without obtaining the landowner’s permission, you could face legal consequences. Trespassing is a serious offence, and the landowner has the right to take legal action.
Legal Consequences of Trespassing:
- Fines or criminal charges could be imposed if you use someone’s land without consent for takeoff or landing.
- Property Owners’ Rights: If a landowner notices drone activity on their property without permission, they have the right to ask the operator to leave and take legal action if necessary.
Sky Scan Surveys: Safe, Legal, and Responsible Drone Operations
At Sky Scan Surveys, we are committed to complying with all drone regulations and ensuring that our operations respect the privacy and rights of property owners. Here’s how we ensure responsible drone operations:
- Obtaining Permission: We always secure the necessary permissions from landowners before conducting any operations on private property.
- Data Protection: We comply with GDPR and ensure that all personal data collected via drone footage is securely stored and protected.
- CAA Compliance: We ensure all our pilots are fully certified and our drones are registered with the CAA.
- Insurance: Our operations are fully insured, covering any potential third-party liabilities.


Frequently Asked Questions
Can I fly a drone over private property or land in the UK?
Yes, it is legal to fly a drone over private property or land in the UK, as long as you comply with CAA regulations, including obtaining permission from the landowner for takeoff and landing.
Do I need permission to land my drone on private property?
Yes, you must obtain explicit permission from the landowner before landing or taking off on their private property. Without consent, this could be considered trespassing.
What are the privacy laws for drone footage in the UK?
If your drone captures identifiable data, such as images or videos of individuals or private property, it is considered personal data under GDPR. You must inform individuals if data is being collected and obtain consent if necessary.
What is the maximum height I can fly my drone in the UK?
Drones must be flown below 400 feet (120 metres) in the UK to comply with aviation regulations.
Do I need to register my drone in the UK?
Yes, drones equipped with cameras or over a certain weight must be registered with the CAA, and operators must pass a competency test to ensure safe flying.
Conclusion
Flying drones over private property in the UK is legal, but it’s crucial to comply with the CAA regulations, obtain landowner permission, and respect privacy laws. By following these guidelines, you can operate your drone safely and legally while avoiding potential legal issues. At Sky Scan Surveys, we ensure our drone operations are always fully compliant with UK law and privacy standards.