What is Drone Surveying?
Drone surveying is the process of using unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to capture aerial data for mapping, analysis, and inspections. It has revolutionized industries such as construction, agriculture, real estate, and infrastructure by providing high-precision data collection in a cost-effective and efficient manner.
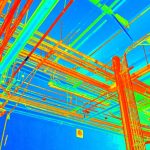
Equipped with advanced cameras, LiDAR sensors, and GPS technology, drones can create accurate 3D maps, elevation models, and orthomosaic images. Compared to traditional surveying methods, drone surveying offers quicker turnaround times, improved safety, and enhanced data accuracy.
How Does Drone Surveying Work?
Drone surveying involves several key steps:
- Planning and Flight Path Design – Surveyors use specialized software to create a flight plan that covers the target area while ensuring optimal data capture.
- Data Collection – The drone flies over the designated area, capturing high-resolution images, LiDAR scans, or thermal data depending on the purpose of the survey.
- Data Processing – The collected images and data are processed using photogrammetry software to generate 3D models, topographic maps, and point clouds.
- Analysis and Reporting – The final outputs are analyzed for various applications such as construction site progress tracking, land measurements, or infrastructure assessments.

Applications of Drone Surveying
Drone surveying has numerous applications across different industries:
1. Construction and Infrastructure
Drones are widely used for site planning, progress monitoring, and quality inspections. By providing real-time aerial data, they help project managers track developments, detect potential issues, and enhance decision-making.
2. Land Surveying and Mapping
Drones enable fast and precise mapping of large land areas. Traditional land surveys can take days, whereas drone surveys provide results within hours. This is crucial for urban planning, property assessments, and land development projects.
3. Drone Roof Inspection
Roof inspections using drones are safer and more efficient than manual methods. With high-resolution cameras and thermal imaging, drones can detect damages, leaks, and structural weaknesses without requiring physical access to rooftops.
4. Agriculture and Forestry
Drone technology is transforming modern farming through precision agriculture. Farmers use drones to monitor crop health, assess soil conditions, and optimize irrigation. In forestry, drones help track deforestation and tree health.
5. Mining and Quarrying
Drones provide accurate volumetric measurements of stockpiles and terrain mapping for mining operations. This improves resource estimation, safety, and operational efficiency.
6. Disaster Management and Environmental Monitoring
Drones play a crucial role in disaster response, offering rapid assessments of affected areas after floods, wildfires, or earthquakes. They also aid in environmental monitoring, tracking deforestation, and detecting illegal mining activities.
Benefits of Drone Surveying
- Cost-Effective – Reduces the need for expensive ground-based surveying equipment and manpower.
- Time-Saving – Captures data faster than traditional surveying techniques.
- Improved Accuracy – High-resolution imaging and GPS technology enhance precision.
- Enhanced Safety – Eliminates the need for surveyors to access hazardous locations.
- Scalability – Drones can survey large areas quickly, making them ideal for extensive projects.
Drone Surveying vs. Traditional Surveying
| Feature | Drone Surveying | Traditional Surveying |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Fast data collection | Slower process |
| Cost | Lower operational costs | Higher labor and equipment costs |
| Accuracy | High precision with GPS & LiDAR | High but time-consuming |
| Accessibility | Can reach remote areas | Limited by terrain |
Equipment Used in Drone Surveying
To achieve precise and reliable results, drone surveying requires specialized equipment, including:
- Surveying Drones – Fixed-wing or multirotor UAVs designed for mapping and inspections.
- High-Resolution Cameras – Capture sharp images for photogrammetry.
- LiDAR Sensors – Used for generating accurate 3D models.
- Thermal Cameras – Ideal for infrastructure assessments and environmental monitoring.
- GPS and RTK Systems – Enhance positioning accuracy.
- Surveying Software – Tools like Pix4D, DroneDeploy, and Agisoft Metashape process data into actionable insights.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Before conducting a drone survey, it’s essential to comply with local aviation regulations. Some key considerations include:
- Drone Pilot Certification – Many countries require drone operators to obtain a commercial drone license.
- Flight Restrictions – Ensure compliance with no-fly zones and airspace regulations.
- Data Privacy – Adhere to privacy laws when capturing aerial data.
- Insurance – Consider liability insurance for commercial drone operations.

Future of Drone Surveying
As drone technology continues to evolve, we can expect significant advancements such as:
- AI-Powered Data Analysis – Automated interpretation of survey data for faster decision-making.
- Improved Battery Life – Longer flight times for extended surveys.
- Enhanced Sensor Technology – More precise LiDAR and thermal imaging capabilities.
- Integration with BIM and GIS – Seamless collaboration between drone data and digital models.
Conclusion
Drone surveying is transforming data collection across various industries, offering unparalleled accuracy, efficiency, and cost savings. Whether for drone roof inspection, land mapping, or drone videography, UAVs provide an innovative solution for modern surveying needs. As technology advances, drone surveying will continue to play a vital role in infrastructure development, environmental monitoring, and beyond.