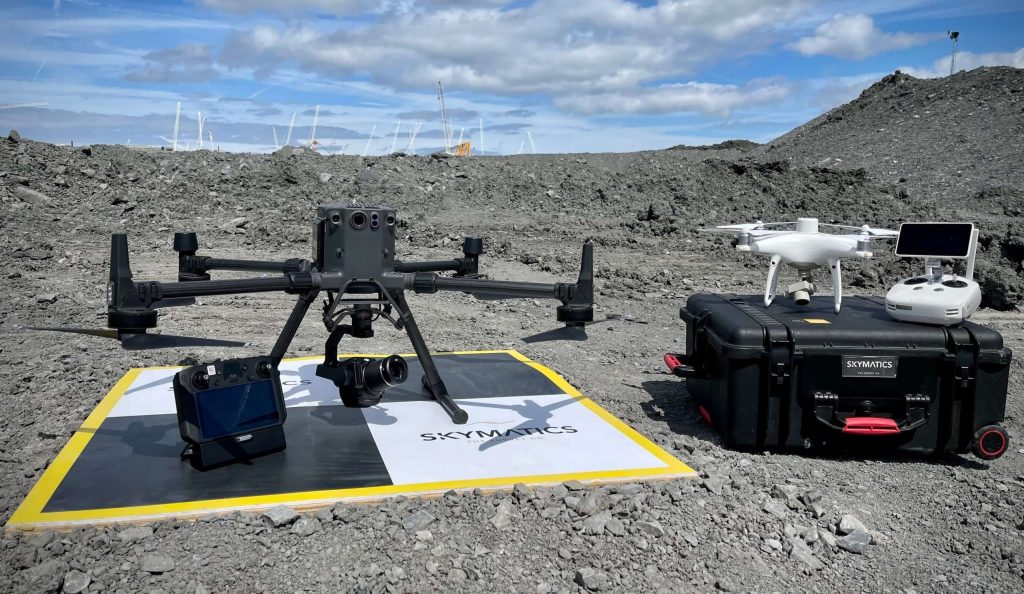
Drone surveys and aerial mapping make use of vehicles (UAVs) with sensors pointing downward such, as LIDAR payloads, RGB cameras or multispectral imaging systems to collect important data. When using an RGB camera on a drone survey the ground is photographed from angles. Each picture is accurately marked with coordinates.
This information is then utilised by photogrammetry software to create geo referenced orthomosaics, detailed 3D models or elevation models of the project area. These maps allow for obtaining details like volume measurements and precise distances.
Drones set themselves apart from satellite images or manned aircraft due to their ability to fly at lower altitudes. This feature results in capturing data with clarity and precision at a fraction of the cost. Additionally drones can operate independently of weather conditions making them unaffected by factors like rain or cloud cover.
WHAT DOES A DRONE SURVEY/ aerial mapping ENTAIL?
A drone survey utilises drones equipped with facing sensors, like LIDAR payloads, RGB cameras or multispectral imaging devices. These advanced tools enable us to gather information from a viewpoint.
When conducting a drone survey, with an RGB camera the ground is carefully photographed from perspectives. Each picture is accurately labeled with coordinates. Innovative photogrammetry software then processes this data to create geo referenced orthomosaics, detailed 3D models and high quality elevation maps of the designated area. These maps serve as tools that enable us to gather information like volume measurements and precise distances.
What makes drone surveys unique compared to methods such as satellite imagery or manned aircraft is their capability to fly at much lower altitudes. This results in capturing data with resolution and accuracy at a cost. Additionally drones are not limited by weather conditions making them unaffected by factors like rain or cloud cover. The outcome? Unmatched. Dependability.
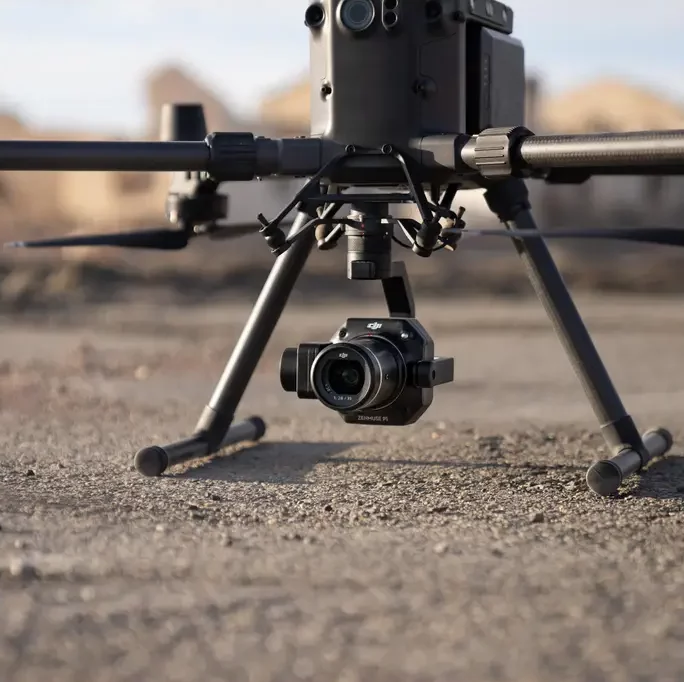

Exploring Drone/ aerial Mapping
Drone mapping involves representing data based on relationships. Drones in construction play a role in capturing aerial images which are then seamlessly combined using specialised mapping software to create an integrated composite image. This process also produces visuals and digital elevation models accessible, in CAD and GIS formats.
Drones are used to map properties, hard to reach areas and complex structures in cases where traditional survey methods are not practical or feasible, like heritage sites and quarries.
WHY CHOOSE DRONE SURVEYING AND AERIAL MAPPING?
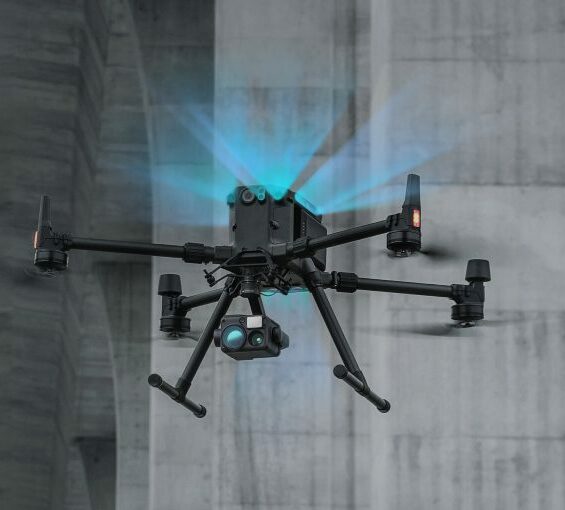

- Provide Accurate and Reliable Data: A single drone mission produces a range of measurements that can be easily converted into formats such as point clouds, Digital Terrain Models (DTM) contour lines, Digital Surface Models (DSM) orthomosaics and more. Each pixel on the map or each point on the 3D model contains 3D geographic information.
- Provide Accurate and Comprehensive Data Quickly: A dedicated aerial survey drone quickly captures survey images and data for large scale projects within timeframes. Aerial surveys are essential for quantity assessments. Ensuring compliance.
- Ability to Map Inaccessible Areas: Aerial mapping drones offer flexibility. They can navigate any terrain, including areas, steep slopes or rugged landscapes that present challenges, for traditional measurement methods.
- Safely Monitor Your Projects Progress: Drones allow you to remotely monitor your projects progress enhancing both efficiency and safety in the monitoring process.